区块链技术探索(二), 打造我们自己的比特币
让我们用匠人的精神设计实现一款让人爱不释手,欲罢不能的产品, 这款产品的分类恰好是货币.
Talk is cheap, show me the code, 让我们从最简单的地方出发: 模仿中本聪的比特币.
项目的代码在 https://github.com/baya/mybt_coin
1. 区块链的存储
在 构造比特币的创世区块 这篇文章中我们把生成的创世区块写到了一个叫 kyk-gens-block.dat 的文件中,这时候我们已经初步完成区块链的存储, 现在我们要为其加上索引, 在比特币的世界里, 使用了 LevelDB[1] 来存储这些索引, 设计索引是一件比较精巧细致的活, 我们可以参考 Bitcoin Core Data Storage[2] 用自己的代码来一步步实现索引.
1.1 比特币的后端存储结构
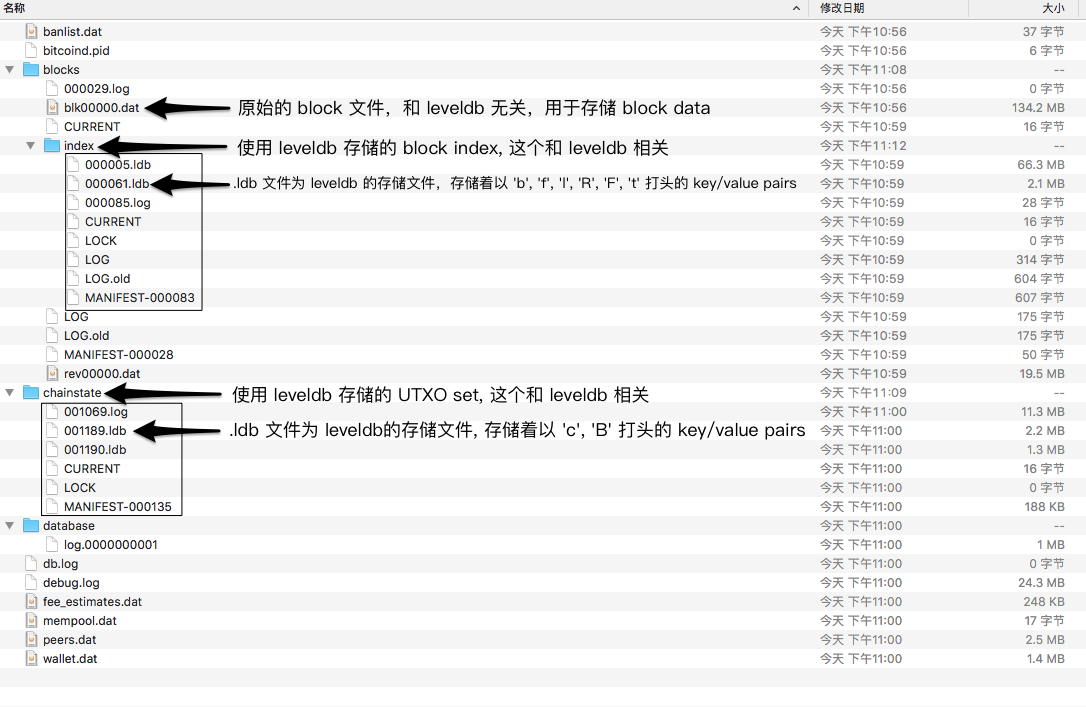
Block index (leveldb)[9]
Key-value pairs
Inside the actual LevelDB, the used key/value pairs are:
'b' + 32-byte block hash -> block index record. Each record stores:
* The block header
* The height.
* The number of transactions.
* To what extent this block is validated.
* In which file, and where in that file, the block data is stored.
* In which file, and where in that file, the undo data is stored.
'f' + 4-byte file number -> file information record. Each record stores:
* The number of blocks stored in the block file with that number.
* The size of the block file with that number ($DATADIR/blocks/blkNNNNN.dat).
* The size of the undo file with that number ($DATADIR/blocks/revNNNNN.dat).
* The lowest and highest height of blocks stored in the block file with that number.
* The lowest and highest timestamp of blocks stored in the block file with that number.
'l' -> 4-byte file number: the last block file number used.
'R' -> 1-byte boolean ('1' if true): whether we're in the process of reindexing.
'F' + 1-byte flag name length + flag name string -> 1 byte boolean ('1' if true, '0' if false): various flags that can be on or off. Currently defined flags include:
* 'txindex': Whether the transaction index is enabled.
't' + 32-byte transaction hash -> transaction index record. These are optional and only exist if 'txindex' is enabled (see above). Each record stores:
* Which block file number the transaction is stored in.
* Which offset into that file the block the transaction is part of is stored at.
* The offset from the start of that block to the position where that transaction itself is stored.
The UTXO set (chainstate leveldb)[10]
Key-value pairs
The records in the chainstate levelDB are:
'c' + 32-byte transaction hash -> unspent transaction output record for that transaction. These records are only present for transactions that have at least one unspent output left. Each record stores:
* The version of the transaction.
* Whether the transaction was a coinbase or not.
* Which height block contains the transaction.
* Which outputs of that transaction are unspent.
* The scriptPubKey and amount for those unspent outputs.
'B' -> 32-byte block hash: the block hash up to which the database represents the unspent transaction outputs.
下面我们要做的工作就是将上面的 ‘b’, ‘f’, ‘l’, ‘R’, ‘F’, ‘t’, ‘c’, ‘B’ 这 8 种类型的 key/value pairs 从 Block index (leveldb) 和 chainsate (leveldb) 数据库中正确的读取出来,并将对应的 value 解析出来. 作为热身我们先写一个简短的程序来熟悉下 leveldb.
1.1.1 leveldb 热身
leveldb 中几乎所有的 c++ 接口都有对应的 c 接口, c 接口在 leveldb/c.h 中定义.
在程序 level_db_api_debug.c 中,我们对 leveldb 中的 打开数据库, 读, 写, 批量写, 删除, 迭代 等 api 进行了实验, 程序中以 leveldb
开头的函数和数据结构都来自于 leveldb/c.h. 用于检查错误的宏: check 则来自于 dbg.h 文件,这个和 leveldb 没有关系。
为了编译运行程序level_db_api_debug.c,我们首先: git clone git@github.com:baya/mybt_coin.git, 然后 cd mybt_coin,
$ make
$ make dbg
$./debug/level_db_api_debug.out
get value: 123 from key: abc, value len: 4
get value: bar from key: foo, value len: 4
key=foo value=bar
key=foo1 value=bar1
key=foo2 value=bar2
key=foo4 value=bar4
1.1.2 读取 ‘b’, ‘f’, ‘l’, ‘R’, ‘F’, ‘t’, ‘c’, ‘B’ key/value pairs
1. 读取 ‘b’ key
'b' + 32-byte block hash
编译运行程序:
$ make dbg
$ ./debug/read_b_key_debug.out 0000000099c744455f58e6c6e98b671e1bf7f37346bfd4cf5d0274ad8ee660cb
其中 read_b_key_debug.out 程序接收一个 block hash 作为参数.
输出:
bkey : 62cb60e68ead74025dcfd4bf4673f3f71b1e678be9c6e6585f4544c79900000000
raw value : 889271cd101d0100808cbf1199b74701000000a7c3299ed2475e1d6ea5ed18d5bfe243224add249cce99c5c67cc9fb00000000601c73862a0a7238e376f497783c8ecca2cf61a4f002ec8898024230787f399cb575d949ffff001d3a5de07f
wVersion: 150001
nHeight: 10000
nStatus: 29
nTx: 1
nFile: 0
nDataPos: 2318353
nUndoPos: 433223
Following is Block Header:
nVersion:1
PrevHash : 00000000fbc97cc6c599ce9c24dd4a2243e2bfd518eda56e1d5e47d29e29c3a7
hashMerkleRoot : 9c397f783042029888ec02f0a461cfa2cc8e3c7897f476e338720a2a86731c60
nTime:1238988213
nBits:1d00ffff
nNonce:2145410362
‘b’ key 的构造步骤: 首先将 block hash 的字节倒序得到: cb60e68ead74025dcfd4bf4673f3f71b1e678be9c6e6585f4544c79900000000, 然后将 ‘b’ 的字节 0x62 作为首位与前者合并就得到了 ‘b’ key.
‘b’ key 对应的 raw value 的格式如下图所示:

下面的这些数据是通过 varint 编码的,但是这个 varint[13] 和以前的 varint[12] 不一样,
// wallet version
int wVersion = 0;
//! height of the entry in the chain. The genesis block has height 0
int nHeight = 0;
//! Verification status of this block.
uint32_t nStatus = 0;
//! Number of transactions in this block.
//! Note: in a potential headers-first mode, this number cannot be relied upon
unsigned int nTx = 0;
//! Which # file this block is stored in (blk?????.dat)
int nFile = 0;
//! Byte offset within blk?????.dat where this block's data is stored
unsigned int nDataPos = 0;
//! Byte offset within rev?????.dat where this block's undo data is stored
unsigned int nUndoPos = 0;
它们的编码和解码方式如下,
编码:
size_t pack_varint(uint8_t *buf, int n)
{
unsigned char tmp[(sizeof(n)*8+6)/7];
int len=0;
while(1) {
tmp[len] = (n & 0x7F) | (len ? 0x80 : 0x00);
if (n <= 0x7F)
break;
n = (n >> 7) - 1;
len++;
}
kyk_reverse_pack_chars(buf, tmp, len+1);
return len+1;
}
解码:
size_t read_varint(const uint8_t *buf, size_t len, uint32_t *val)
{
uint32_t n = 0;
size_t i = 0;
while(i < len) {
unsigned char chData = *buf;
buf++;
n = (n << 7) | (chData & 0x7F);
if (chData & 0x80) {
i++;
n++;
} else {
*val = n;
i++;
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
2. 读取 ‘f’ key
'f' + 4-byte file number
编译运行程序:
$ make dbg
$ ./debug/read_f_key_debug.out 1
输出:
fkey : 6601000000
raw value : d703befd9860878acc1186a57e87804983ecc7e61b83eee7f21d
nBlocks: 11267 (number of blocks stored in file)
nSize: 134188256 (number of used bytes of block file)
nUndoSize: 16967313 (number of used bytes in the undo file)
nHeightFirst: 119678 (lowest height of block in file)
nHeightLast: 131273 (highest height of block in file)
nTimeFirst: 1303524251 (earliest time of block in file)
nTimeLast: 1308244381 (latest time of block in file)
‘f’ key 对应的 raw value 的格式如下所示, 它们都是以 varint[13] 的格式写入到 leveldb 中的.
unsigned int nBlocks; //!< number of blocks stored in file
unsigned int nSize; //!< number of used bytes of block file
unsigned int nUndoSize; //!< number of used bytes in the undo file
unsigned int nHeightFirst; //!< lowest height of block in file
unsigned int nHeightLast; //!< highest height of block in file
uint64_t nTimeFirst; //!< earliest time of block in file
uint64_t nTimeLast; //!< latest time of block in file
3. 读取 ‘l’ key
编译运行程序:
$ make dbg
$ ./debug/read_l_key_debug.out
输出:
lkey : 6c
raw value : 60000000
nFile: 96 (the last block file number used)
4. 读取 ‘R’ key
编译运行程序:
$ make dbg
$ ./debug/read_r_key_debug.out
输出:
Rkey : 52
raw value :
nReindex: 0 (not reindexing)
5. 读取 ‘F’ key
'F' + 1-byte flag name length + flag name string
编译运行程序:
$ make dbg
$ ./debug/read_cap_f_key_debug.out
输出:
Fkey : 46077478696e646578
raw value : 30
txindex: false
上面的 30 其身是字符 ‘0’ 的 Hex 表示值, 字符 ‘0’ 用于表示 false, 字符 ‘1’ 用于表示 true.
6. 读取 ‘t’ key
编译运行程序:
$ make dbg
$./debug/read_t_key_debug.out 4a5e1e4baab89f3a32518a88c31bc87f618f76673e2cc77ab2127b7afdeda33b
输出:
No record Found
貌似我下载的比特币钱包没有对交易进行索引.
7. 读取 ‘c’ key[14]
'c' + 32-byte transaction hash
编译运行程序:
$ make dbg
$./debug/read_c_key_debug.out 4a5e1e4baab89f3a32518a88c31bc87f618f76673e2cc77ab2127b7afdeda33b
输出:
ckey : 633ba3edfd7a7b12b27ac72c3e67768f617fc81bc3888a51323a9fb8aa4b1e5e4a
No record Found
8. 读取 ‘B’ key
输出:
Bkey : 42
raw value : 9acae02f84a810af603bc486996f273b9394ab1b308e56402d3f7171111520f9
得到的 raw value 不是一个 block hash, 不知道是什么原因.
1.2 以比特币为参照, 存储我们自己创建的创世区块
通过程序 wallet2.c 封装了初始化数据库, 读取写入 block 等工作.
编译运行程序:
$ make
$ make wallet2
初始化钱包,
./wallet2.out init
这条命令会在当前目录下构建一个钱包, 其中 blk00000.dat 里存储着我们自己的创世区块的原始数据.
my_wallet2
└── blocks
├── blk00000.dat
└── index
├── 000005.ldb
├── 000026.log
├── CURRENT
├── LOCK
├── LOG
├── LOG.old
└── MANIFEST-000025
通过 block hash 查询创世区块,
./wallet2.out getblock 0000876c9ef8c1f8b2a3012ec1bdea7296f95ae21681799f8adf967f548bf8f3
查询结果:
wVersion: 1
nHeight: 0
nStatus: 24
nTx: 1
nFile: 0
nDataPos: 8
nUndoPos: 0
Following is Block Header:
nVersion: 1
PrevHash : 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
hashMerkleRoot : b76d27da4abf50387dd70f5d6cc7e4df1d54722631cbbfdd292463df77aa0dbd
nTime: 1504483200
nBits: 1f00ffff
nNonce: 65119
现在我们已经将我们自己的创世区块存储到了自己构建的数据库中了, 在后面我们将进行 创建交易, 生成新的区块 等一系列工作.
2. 交易和区块的验证
首先我们看下 “tx” messages 的验证规则[15],
2.1 交易的验证规则
1. Check syntactic correctness;
检查的消息语法是否正确.
2. Make sure neither in or out lists are empty;
输入和输出不能为空, 也就是说当你发起一笔交易, 你必须告诉比特币网络这笔交易的钱是从哪里来的,要到哪里去.
3. Size in bytes <= MAX_BLOCK_SIZE;
消息的大小不能超过区块的最大容量, 因为消息中的交易最终是要被打包到区块中, 如果一笔交易的大小超过了区块的大小也就意味着这笔交易无法被打包到交易中去了. 目前区块的最大容量是 1M, 而基于纽约共识(New York Agreement)的比特币升级方案 SegWit2x[18] 的一项主要内容就是将区块的最大容量提升到 2M, 就是这么一个看似非常简单的扩容却要引起比特币网络的分裂, 对于我这种传统应用(中心化应用)的开发者来说这种分裂(hard fork)现象简直不可思议, 就好像我把数据库中的某个表增加了几个字段,或者把数据库从 mongodb 迁移到了 postgresql 就会造成我的应用分裂成两个应用一样,一个应用使用 mongodb, 另外一个应用使用 postgresql, 然后我的用户也跟着会分成两个派别,一种支持 mongodb, 一种支持 postgresql, 当然现实的情况是我的用户丝毫不关心我在后台使用了哪种数据库, 他们甚至可能都不知道世界上有数据库这种东西,他们只关心我的应用是否好用,是否安全稳定. 但是在比特币的世界里, 区块的大小确实是成为了一种规则,而我在 构造比特币的创世区块 这篇文章中 的第一段里也提到过:
在比特币的世界里, 规则塑造本尊,改变规则预示着分裂
分裂也不是什么坏事, 物竞天择,适者生存.
4. Each output value, as well as the total, must be in legal money range;
交易的输出金额和总金额应该是一个合法的值, 比如不能为 0, 不能为负数, 比特币的最小单位是 0.00000001(一亿分之1), 称为 “1聪”, 输出的金额也不应该小于 “1聪”, 也不能大于 2100 万个币.
5. Make sure none of the inputs have hash=0, n=-1 (coinbase transactions)
“tx” message 里不能包含 coinbase 交易(即造币交易), coinbase 交易只能通过旷工挖矿生成区块时产生, 旷工可以通过广播区块,将区块中包含的 coinbase 交易广播给其他比特币节点.
6. Check that nLockTime <= INT_MAX[19], size in bytes >= 100[20], and sig opcount <= 2[21]
7. Reject “nonstandard” transactions: scriptSig doing anything other than pushing numbers on the stack, or scriptPubkey not matching the two usual forms[22]
scriptSig 的结构是 <sig> <pubKey>, scriptSig 的逻辑就是将 <sig> 和 <pubKey> 压入到栈中以供解锁 scriptPbkey 除此以外再无其他功能.
8. Reject if we already have matching tx in the pool, or in a block in the main branch
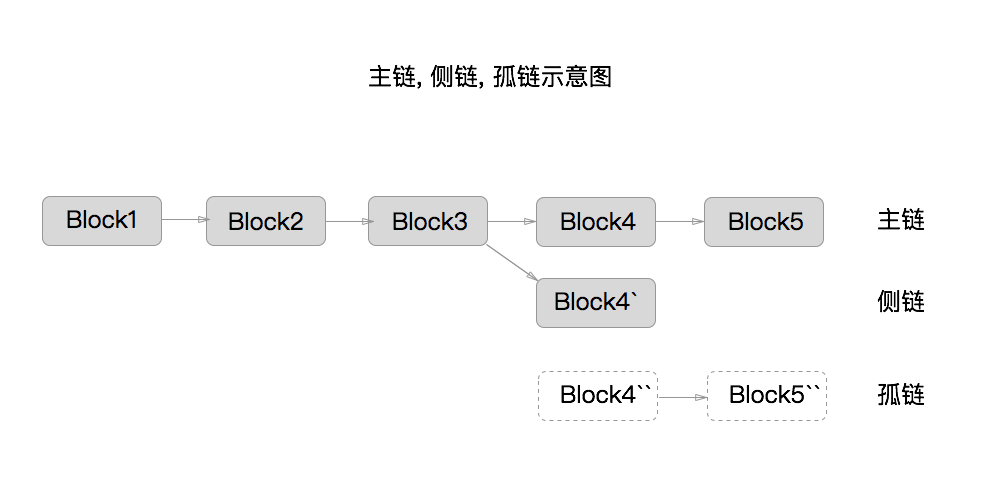
如果交易池中已经有同一笔交易了,或者区块的主链(就是最长的那条链)上有同一笔交易了,我们就拒绝这条交易.
9. For each input, if the referenced output exists in any other tx in the pool, reject this transaction.[23]
简单地讲就是交易的输入不能建立在一个已经消费的输出上. 为了更直观地理解这条规则,我画了一张图, 这条规则的主要目的就是为了防御双花攻击, 当然这种防御方式是建立在 POW 的基础上的.
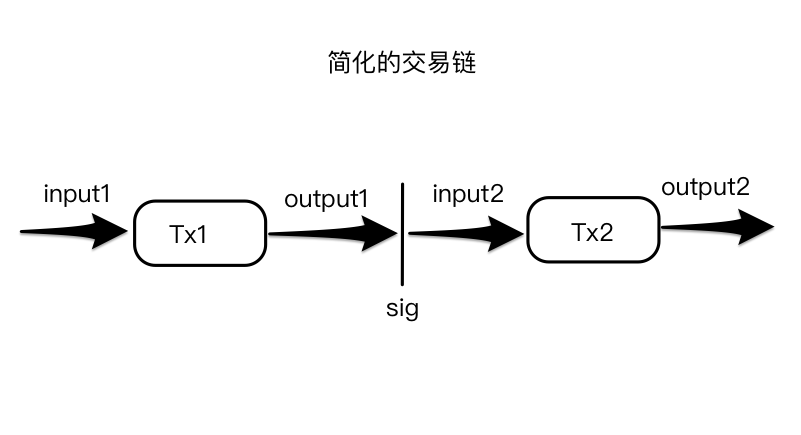
上图是一个简化后的交易链,虽然实际情况上一笔交易可能会有多个 input 和多个 output, 但是简化后的交易链不影响我们分析规则 9.
按图中描述,如果我们要构造一笔新的交易,那么这笔新交易的 input 显然不能和 output1 对接, 因为 output1 已经被 Tx2 的 input2 所使用了, 这笔新的交易的 input 可以和 Tx2 的 output2 对接,因为 output2 没有被使用, 当然交易的构造者需要有能够解锁 output2 的私匙.
10.For each input, look in the main branch and the transaction pool to find the referenced output transaction. If the output transaction is missing for any input, this will be an orphan transaction. Add to the orphan transactions, if a matching transaction is not in there already.
如果交易的 input 对接的 output 所属的交易缺失任何一个输入, 那么这笔交易要被纳入到孤交易集合(orphan transactions)中, 当然如果这笔交易已经被纳入到孤交易中去了,那么就不用做重复的纳入工作了.
为什么会有孤交易这种奇怪的东西出现呢? 让我们通过一张图来了解这一现象,
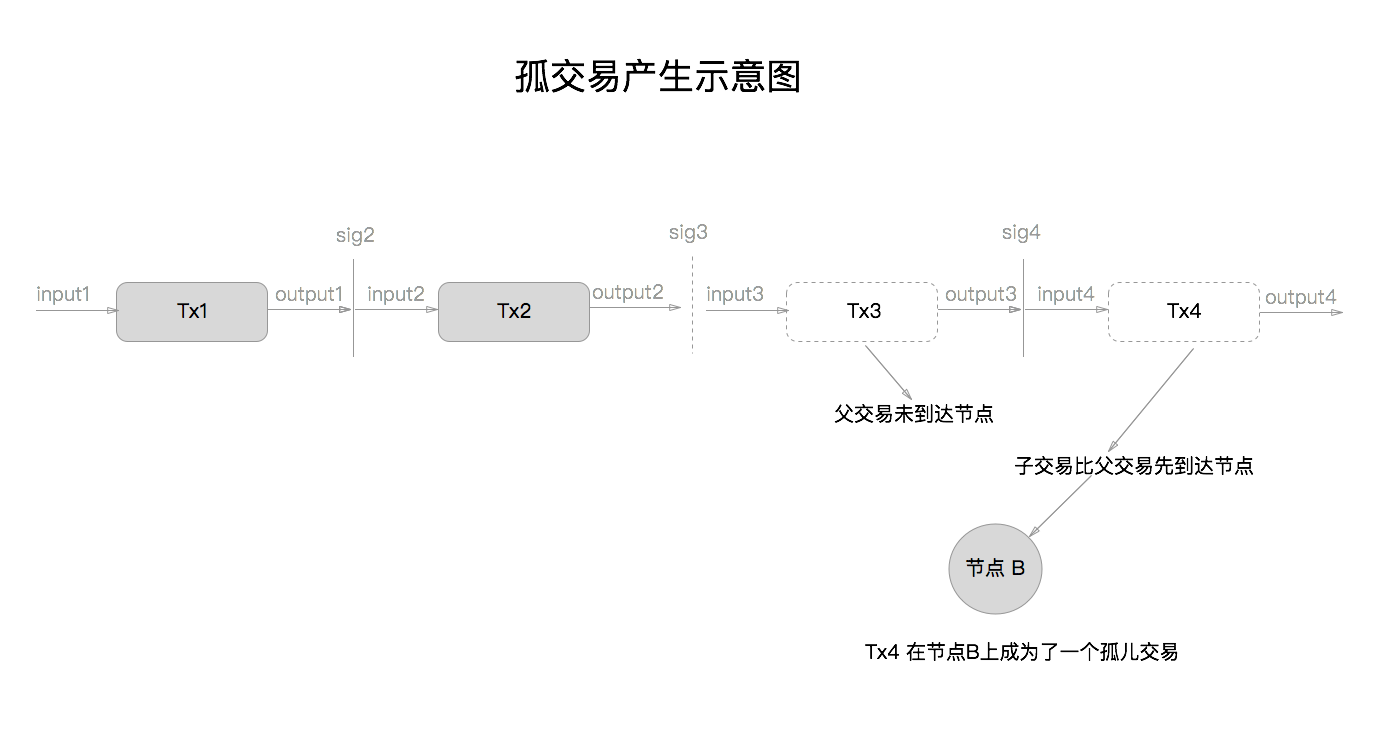
如果有恶意的用户伪造大量的,恶意的,根本没有父交易的孤交易来攻击节点, 这种攻击可能会导致节点瘫痪, 所以节点会限制孤交易池的大小, 并且会清理过期的孤交易.
11. For each input, if the referenced output transaction is coinbase (i.e. only 1 input, with hash=0, n=-1), it must have at least COINBASE_MATURITY (100) confirmations; else reject this transaction
如果交易的 input 对接的 output 来自 coinbase transaction, 那么这个 coinbase transaction 必须是经过了 100 次确认才能使用, 简单的说就是这个 coinbase transaction 所在的区块上面至少要有一个 100 个区块, 比如某个 coinbase transaction 所在的区块高度是 1000, 那么要必须等到主链的高度增加到 1100 个区块后才能使用这个 coinbase transaction 里的 output.
12. For each input, if the referenced output does not exist (e.g. never existed or has already been spent), reject this transaction[24]
如果交易的 input 对接的 output 已经被花费或者根本不存在, 那么拒绝这笔交易.
13. Using the referenced output transactions to get input values, check that each input value, as well as the sum, are in legal money range
和规则 14 关联起来理解, input 本身没有 value, input 通过解锁相关的 output 获得 value.
14. Reject if the sum of input values < sum of output values
在一笔交易中,它的 input value 是它解锁的对接 output 的 value, 如果你分析过 Txin 的数据结构,你就会发现 Txin 里并没有 value 或者 amout 之类的字段, Txin 的作用就是解锁对接交易的 output, 将对接交易的 output 的 value 释放给本交易的 output. 通过下面的图我们可以更加直观地理解规则 14,
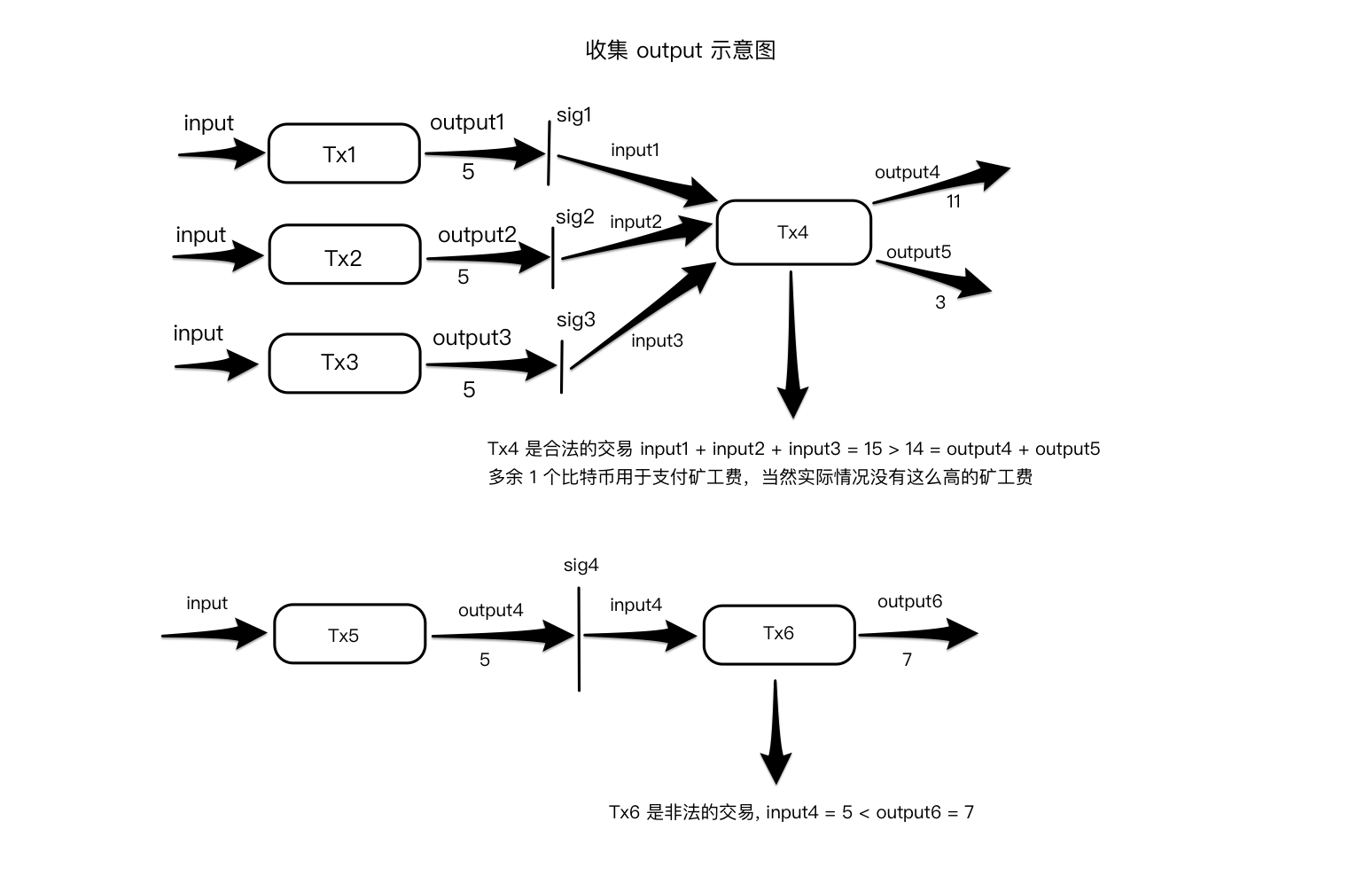
比特币中的 output 只能作为一个整体被解锁,一旦被解锁,它里面的 value 会被全部释放.
15. Reject if transaction fee (defined as sum of input values minus sum of output values) would be too low to get into an empty block
16. Verify the scriptPubKey accepts for each input; reject if any are bad
input 中的 scriptSig 解锁对接的 output 中的 scriptPubKey, 如果无法解锁则拒绝交易.
17. Add to transaction pool[17]
18. “Add to wallet if mine”
19. Relay transaction to peers
传播交易到其他节点
20. For each orphan transaction that uses this one as one of its inputs, run all these steps (including this one) recursively on that orphan
2.2 区块的验证规则
These messages hold a single block.[15]
1. Check syntactic correctness
2. Reject if duplicate of block we have in any of the three categories[27]
the three categories, 表示的 3 种类型是: blocks in the main branch, blocks on side branches off the main branch, orphan blocks
3. Transaction list must be non-empty
4. Block hash must satisfy claimed nBits proof of work
block hash 前面的 0 的个数需要和 block header 中的 Bits 字段相匹配,从而通过工作量的证明.
5. Block timestamp must not be more than two hours in the future
6. First transaction must be coinbase (i.e. only 1 input, with hash=0, n=-1), the rest must not be
区块中的第一交易必须为 coinbase 交易,并且只包含一笔 coinbase 交易.
7. For each transaction, apply “tx” checks 2-4
8. For the coinbase (first) transaction, scriptSig length must be 2-100
9. Reject if sum of transaction sig opcounts > MAX_BLOCK_SIGOPS
10. Verify Merkle hash
11. Check if prev block (matching prev hash) is in main branch or side branches. If not, add this to orphan blocks, then query peer we got this from for 1st missing orphan block in prev chain; done with block
12. Check that nBits value matches the difficulty rules
13. Reject if timestamp is the median time of the last 11 blocks or before
14. For certain old blocks (i.e. on initial block download) check that hash matches known values
15. Add block into the tree. There are three cases: 1. block further extends the main branch; 2. block extends a side branch but does not add enough difficulty to make it become the new main branch; 3. block extends a side branch and makes it the new main branch.
16. For case 1, adding to main branch:
1. For all but the coinbase transaction, apply the following:
1. For each input, look in the main branch to find the referenced output transaction. Reject if the output transaction is missing for any input.
2. For each input, if we are using the nth output of the earlier transaction, but it has fewer than n+1 outputs, reject.
3. For each input, if the referenced output transaction is coinbase (i.e. only 1 input, with hash=0, n=-1), it must have at least COINBASE_MATURITY (100) confirmations; else reject.
4. Verify crypto signatures for each input; reject if any are bad
5. For each input, if the referenced output has already been spent by a transaction in the main branch, reject
6. Using the referenced output transactions to get input values, check that each input value, as well as the sum, are in legal money range
7. Reject if the sum of input values < sum of output values
2. Reject if coinbase value > sum of block creation fee and transaction fees
3. (If we have not rejected):
4. For each transaction, "Add to wallet if mine"
5. For each transaction in the block, delete any matching transaction from the transaction pool
6. Relay block to our peers
7. If we rejected, the block is not counted as part of the main branch
17. For case 2, adding to a side branch, we don’t do anything.
18. For case 3, a side branch becoming the main branch:
1. Find the fork block on the main branch which this side branch forks off of
2. Redefine the main branch to only go up to this fork block
3. For each block on the side branch, from the child of the fork block to the leaf, add to the main branch:
1. Do "branch" checks 3-11
2. For all but the coinbase transaction, apply the following:
1. For each input, look in the main branch to find the referenced output transaction. Reject if the output transaction is missing for any input.
2. For each input, if we are using the nth output of the earlier transaction, but it has fewer than n+1 outputs, reject.
3. For each input, if the referenced output transaction is coinbase (i.e. only 1 input, with hash=0, n=-1), it must have at least COINBASE_MATURITY (100) confirmations; else reject.
4. Verify crypto signatures for each input; reject if any are bad
5. For each input, if the referenced output has already been spent by a transaction in the main branch, reject
6. Using the referenced output transactions to get input values, check that each input value, as well as the sum, are in legal money range
7. Reject if the sum of input values < sum of output values
3. Reject if coinbase value > sum of block creation fee and transaction fees
4. (If we have not rejected):
5. For each transaction, "Add to wallet if mine"
4. If we reject at any point, leave the main branch as what it was originally, done with block
5. For each block in the old main branch, from the leaf down to the child of the fork block:
1. For each non-coinbase transaction in the block:
1. Apply "tx" checks 2-9, except in step 8, only look in the transaction pool for duplicates, not the main branch
2. Add to transaction pool if accepted, else go on to next transaction
6. For each block in the new main branch, from the child of the fork node to the leaf:
1. For each transaction in the block, delete any matching transaction from the transaction pool
7. Relay block to our peers
19. For each orphan block for which this block is its prev, run all these steps (including this one) recursively on that orphan
2.3 实现矿工节点
2.3.1 比特币网络的难度调整算法(Difficulty Adjustment)
比特币网络每生成 2016 个 block 时就会对全网的 hash 算力进行一次评估,并根据评估结果对全网的 Difficulty[29] 进行调整, 调整的结果可能是增大难度,减小难度,或者保持难度不变. 难度和 hash 运算的次数之间有一个公式:
HashNum = Total / (difficulty_1_target / D)
HashNum 表示运行 hash 计算的次数, Total 表示所有的均匀出现的数字的数量, difficulty_1_target 表示难度为 1 的 target, target 是一个小于 Total 的数字, D 表示难度.
还以骰子为例, 假设我们有一个包含从 0 ~ 999 的数字的骰子, 此时的 Total 是 1000, 抛掷骰子时,每个数字出现的几率是相等的都是千分之一, 我们设定 difficulty_1_target 为 800, 那么抛出一个数小于 800 的概率是 800/1000, 在概率上是要抛 1000/800 次骰子才能得到一个小于 800 的数字, 如果我们提升难度为 10,
那么 target 就变为了 difficulty_1_target / D = 800 / 10 = 80, 那么抛出一个数小于 80 的概率是 80/1000, 在概率统计上要抛 1000/80 次骰子才能得到一个小于 80 的数字.
公式 Total / (difficulty_1_target / D) 的简化形式如下:
HashNum = D * Total / difficulty_1_target
在比特币网络中, Total = 2**256, difficulty_1_target = 0xffff * 2**208, 于是这个公式变成了 D * 2**48 / 0xffff, 这个公式的意思是: 在难度为 D 的条件下, 在概率上, 比特币网络需要要进行 D * 2**48 / 0xffff 次 hash 运算才能算出一个满足难度 D 的 block. 比特币网络的标准出块时间是 10 分钟,
那么比特币网络在难度 D 下的标准算力即为: D * 2**48 / 0xffff / 600 = D * 2**32 / 600. 现在我们可以得到另外一个公式:
其中 H 表示每秒进行 hash 运算的次数,
D = H * 600 / 2 ** 32
于是调整难度的关键就变成了如何计算出 H, 我们知道比特币网络是每 2016 个区块评估一次算力, 在前 2016 个区块段中, 难度是已知的, 生成 2016 个区块所花费的总时间也是已知的,那么可以通过下面的公式评估出当前网络的算力,
H = pervD * 2**32 * 2016 / T
其中 prevD 表示前 2016 个区块的难度(这 2016 个区块的难度是一样的), T 表示生成 2016 个区块总共花的时间这个也是以知的, 这样我们就算出了 H, 然后把 H 代入到公式 D = H * 600 / 2 ** 32 中就可以计算出当前网络需要调整到的难度 D, 这时计算 D 的公式可以变为:
D = prevD * 2016 * 600 / T
公式左右两边同时被 difficulty_1_target 除就变为了,
difficulty_1_target / D = (difficulty_1_target * T )/ (prevD * 2016 * 600)
NextTarget = (PrevTarget * T) / (2016 * 600)
其中 NextTarget = difficulty_1_target / D, PrevTarget = difficulty_1_target / prevD, 我们可以查看 bitcoin 的源码验证我们的求导结果和 bitcoin 是一致的,
https://github.com/bitcoin/bitcoin/blob/master/src/pow.cpp#L49
unsigned int CalculateNextWorkRequired(const CBlockIndex* pindexLast, int64_t nFirstBlockTime, const Consensus::Params& params)
{
if (params.fPowNoRetargeting)
return pindexLast->nBits;
// Limit adjustment step
int64_t nActualTimespan = pindexLast->GetBlockTime() - nFirstBlockTime;
if (nActualTimespan < params.nPowTargetTimespan/4)
nActualTimespan = params.nPowTargetTimespan/4;
if (nActualTimespan > params.nPowTargetTimespan*4)
nActualTimespan = params.nPowTargetTimespan*4;
// Retarget
const arith_uint256 bnPowLimit = UintToArith256(params.powLimit);
arith_uint256 bnNew;
bnNew.SetCompact(pindexLast->nBits);
bnNew *= nActualTimespan;
bnNew /= params.nPowTargetTimespan;
if (bnNew > bnPowLimit)
bnNew = bnPowLimit;
return bnNew.GetCompact();
}
在 bitcoin 的源码中对 T 进行了处理, 其中的 nActualTimespan 即表示 NextTarget = (PrevTarget * T) / (2016 * 600) 中的 T,
if (nActualTimespan < params.nPowTargetTimespan/4)
nActualTimespan = params.nPowTargetTimespan/4;
if (nActualTimespan > params.nPowTargetTimespan*4)
nActualTimespan = params.nPowTargetTimespan*4;
// Retarget
const arith_uint256 bnPowLimit = UintToArith256(params.powLimit);
arith_uint256 bnNew;
bnNew.SetCompact(pindexLast->nBits);
bnNew *= nActualTimespan;
bnNew /= params.nPowTargetTimespan;
这里 bnNew * nActualTimespan / params.nPowTargetTimespan 算出的就是新的 2016 个区块的 target, 这个和 NextTarget = (PrevTarget * T) / (2016 * 600) 效果是一致的.
2.3.2 实验矿工节点
$ make
$ make kyk_miner
$ ./kyk_miner.out # 查看支持的命令
$ ./kyk_miner.out init # 初始化矿工
$ ./kyk_miner.out makeBlock # 生产一个区块, 这个区块包含 100 BTC, 并且只包含一笔 coinbase 交易, 即矿工给自己增加 100 个BTC, 真实的 BTC 网络在后期是不允许这样操作的
输出: maked a new block: 0000f5e6d8700e78989ac97ac12a0c6f216e5ad42a7008ec22298f1d997abe63
$ ./kyk_miner.out queryBlance # 查询拥有的 BTC 数量
输出: 100.000000 BTC
$ ./kyk_miner.out queryBlock 0000f5e6d8700e78989ac97ac12a0c6f216e5ad42a7008ec22298f1d997abe63 # 查询 block 数据
输出:
wVersion: 1
nHeight: 0
nStatus: 24
nTx: 1
nFile: 0
nDataPos: 242
nUndoPos: 0
Following is Block Header:
nVersion: 1
PrevHash : 0000876c9ef8c1f8b2a3012ec1bdea7296f95ae21681799f8adf967f548bf8f3
hashMerkleRoot : 0b527174947e9d808c3d4d2dbf1780be764a53ce22fbc09d124f0e4a02686d43
nTime: 1514128378
nBits: 1f00ffff
nNonce: 64368
$ ./kyk_miner.out makeTx 8 invalidaddress # 向非法地址转账失败
$ ./kyk_miner.out makeTx 8 1KAWPAD8KovUo53pqHUY2bLNMTYa1obFX9 # 向正常的地址转账成功
$ ./kyk_miner.out queryBalance # 查询余额, 因为每当生成一笔交易时,矿工都会创建一个新的 block, 增加 100 BTC, 无矿工费用, 矿工费用可以在 src/kyk_defs.h 文件中设置
输出:
192.000000 BTC
$ ./kyk_miner.out addAddress "a2" # 增加一个 label 为 "a2" 的地址
输出:
Added a new address: 13dqX7yNia35V2dZkM5dMyTExocyPTAbAT
$ ./kyk_miner.out showAddrList # 显示矿工当前拥有的地址
输出:
1GkfyvQod8Bj4nFTrTejdr64kMprqTFSgb
13dqX7yNia35V2dZkM5dMyTExocyPTAbAT
$ ./kyk_miner.out makeTx 9 13dqX7yNia35V2dZkM5dMyTExocyPTAbAT # 矿工给自己控制的地址发送 9 个比特币, 结果是增加 100 个比特币
./kyk_miner.out queryBalance
输出:
292.000000 BTC
$ ./kyk_miner.out serve 8333 # 启动服务
如果陷入了困境,可以删除矿工,重新开始:
$ ./kyk_miner.out delete
3. 参考资料
[1] https://bitcoin.stackexchange.com/questions/28168/what-are-the-keys-used-in-the-blockchain-leveldb-ie-what-are-the-keyvalue-pair What are the keys used in the blockchain levelDB?
[2] https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Bitcoin_Core_0.11_(ch_2):_Data_Storage Bitcoin Core Data Storage
[3] https://bitcoin.stackexchange.com/questions/51387/how-does-bitcoin-read-from-write-to-leveldb/52167#52167 How does Bitcoin read from/write to LevelDB
[4] https://jeiwan.cc/posts/building-blockchain-in-go-part-3/ Building Blockchain in Go. Part 3: Persistence and CLI
[5] https://github.com/google/leveldb/blob/master/doc/impl.md The implementation of leveldb
[6] https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Bitcoin_Core_0.11_(ch_4):_P2P_Network Bitcoin Core 0.11 (ch 4): P2P Network
[7] https://bitcoin.org/en/developer-guide#term-utxo Unspent Transaction Outputs (UTXOs)
[8] http://www.cnblogs.com/pandang/p/7279306.html LevelDB C API 整理分类
[9] https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Bitcoin_Core_0.11_(ch_2):_Data_Storage#Block_index_.28leveldb.29 Block index (leveldb)
[10] https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Bitcoin_Core_0.11_(ch_2):_Data_Storage#The_UTXO_set_.28chainstate_leveldb.29 The UTXO set (chainstate leveldb)
[11] https://github.com/bitcoin/bitcoin/blob/f914f1a746d7f91951c1da262a4a749dd3ebfa71/src/chain.h#L295 Bitcoin Block index SerializationOp
[12] https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Protocol_documentation#Variable_length_integer Variable length integer
[13] 本文的 varint 的解码和编码方式如下, 如果没有特殊说明, 本文的 varint 都按下面的方式进行解码和编码.
size_t read_varint(const uint8_t *buf, size_t len, uint32_t *val)
{
uint32_t n = 0;
size_t i = 0;
while(i < len) {
unsigned char chData = *buf;
buf++;
n = (n << 7) | (chData & 0x7F);
if (chData & 0x80) {
i++;
n++;
} else {
*val = n;
i++;
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
size_t pack_varint(uint8_t *buf, int n)
{
unsigned char tmp[(sizeof(n)*8+6)/7];
int len=0;
while(1) {
tmp[len] = (n & 0x7F) | (len ? 0x80 : 0x00);
if (n <= 0x7F)
break;
n = (n >> 7) - 1;
len++;
}
kyk_reverse_pack_chars(buf, tmp, len+1);
return len+1;
}
[14] https://github.com/bitcoin/bitcoin/blob/d4a42334d447cad48fb3996cad0fd5c945b75571/src/coins.h#L19 Serialized format of UTXO
[15] https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Protocol_rules#.22tx.22_messages Tx and Block message Validation
[16] https://github.com/google/leveldb/blob/master/include/leveldb/c.h Leveldb C API
[17] Note that when the transaction is accepted into the memory pool, an additional check is made to ensure that the coinbase value does not exceed the transaction fees plus the expected BTC value (25BTC as of this writing); coinbase 交易中包含的价值应该等于挖矿产出加交易费. 挖矿产出是4年一个周期减半.
[18] https://github.com/btc1/bitcoin/tree/segwit2x
[19] nLockTime must not exceed 31 bits, as some clients will interpret it incorrectly
[20] A valid transaction requires at least 100 bytes. If it’s any less, the transaction is not valid
[21] The number of signature operands in the signature (no, that is not redundant) for standard transactions will never exceed two
[22] Note that this is not a hard requirement on clients
[23] Note that this is not a hard requirement on clients. The network-enforced rule is that only one transaction spending a particular output can be in the blockchain, thus preventing double-spending. Technically miners can choose which one they want to put into the block they’re working on as long as no other transaction has spent that output either previously in the blockchain, or in the same block. The in-memory transaction pool can technically be managed in whatever way the miner is willing to implement.
[24] This is the protection against double-spending
[25] Note that when the transaction is accepted into the memory pool, an additional check is made to ensure that the coinbase value does not exceed the transaction fees plus the expected BTC value (25BTC as of this writing).
[26] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Double-spending Double-spending
[27] There are 3 categories of blocks:
blocks in the main branch:
the transactions in these blocks are considered at least tentatively confirmed
blocks on side branches off the main branch:
these blocks have at least tentatively lost the race to be in the main branch
orphan blocks:
these are blocks which don't link into the main branch, normally because of a missing predecessor or nth-level predecessor
Blocks in the first two categories form a tree rooted at the genesis block, linked by the prev pointer, which points toward the root. (It is a very linear tree with few and short branches off the main branch.) The main branch is defined as the branch with highest total difficulty, summing the difficulties for each block in the branch.
[28] https://github.com/bitcoinbook/bitcoinbook/blob/second_edition/ch04.asciidoc#base58check_encoding Base58Check Encoding
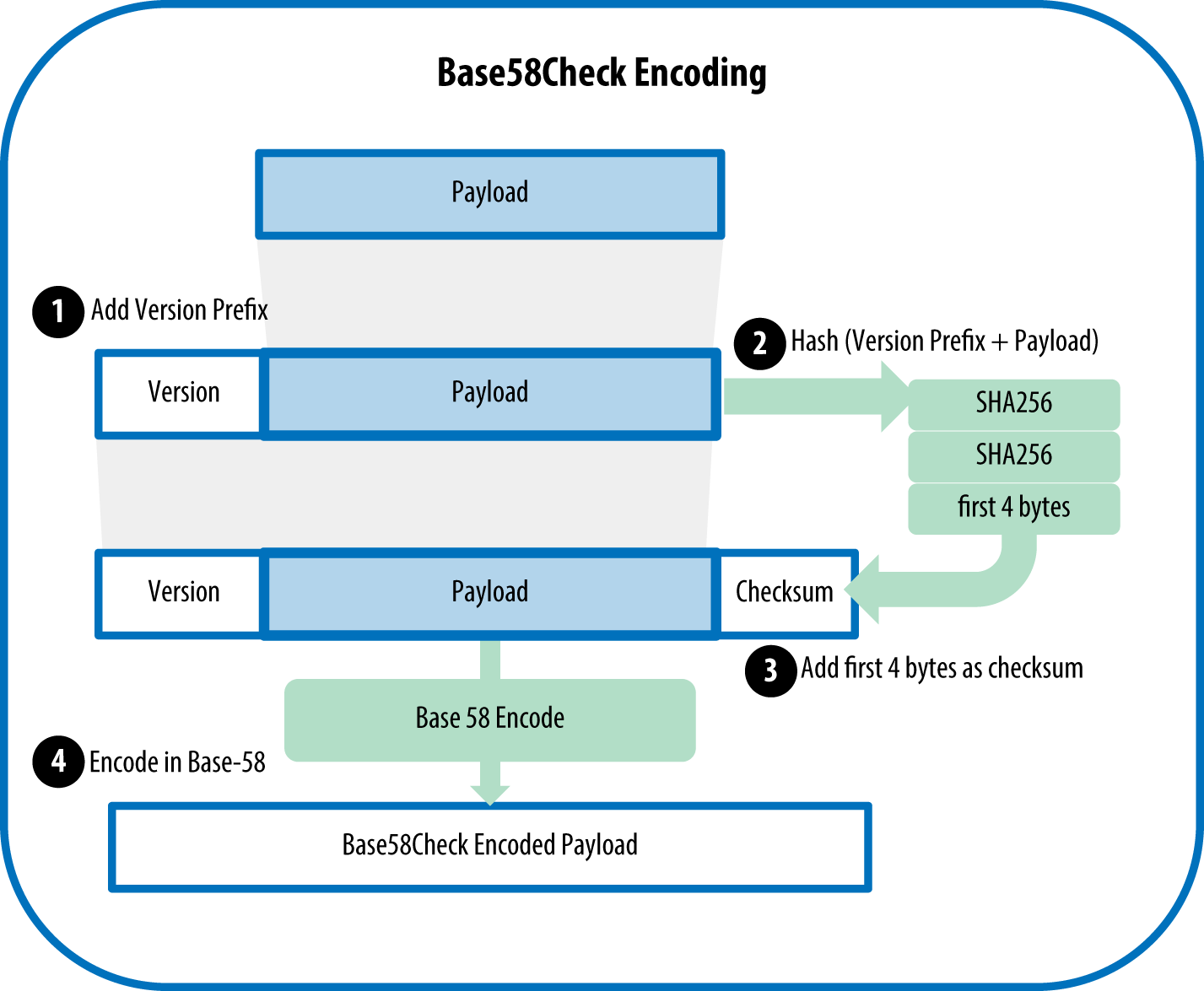
Base58Check version prefix and encoded result examples
| Type | Version prefix (hex) | Base58 result prefix |
|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin Address | 0x00 | 1 |
| Pay-to-Script-Hash Address | 0x05 | 3 |
| Bitcoin Testnet Address | 0x6F | m or n |
| Private Key WIF | 0x80 | 5, K, or L |
| BIP-38 Encrypted Private Key | 0x0142 | 6P |
| BIP-32 Extended Public Key | 0x0488B21E | xpub |
Private key representations (encoding formats)
| Type | Prefix | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Raw | None | 32 bytes |
| Hex | None | 64 hexadecimal digits |
| WIF | 5 | Base58Check encoding: Base58 with version prefix of 128- and 32-bit checksum |
| WIF-compressed | K or L | As above, with added suffix 0x01 before encoding |
Example: Same key, different formats
| Format | Private key |
|---|---|
| Hex | 1e99423a4ed27608a15a2616a2b0e9e52ced330ac530edcc32c8ffc6a526aedd |
| WIF | 5J3mBbAH58CpQ3Y5RNJpUKPE62SQ5tfcvU2JpbnkeyhfsYB1Jcn |
| WIF-compressed | KxFC1jmwwCoACiCAWZ3eXa96mBM6tb3TYzGmf6YwgdGWZgawvrtJ |
关于 WIF 和 WIF-compressed 的实现细节可以参考文件 kyk_base58.c 中的 kyk_base58check 函数, 相关的测试可以查看 kyk_base58_tests.c
[29] https://bitcoin.stackexchange.com/questions/3059/what-is-a-compressed-bitcoin-key What is a compressed Bitcoin key?
A compressed key is just a way of storing a public key in fewer bytes (33 instead of 65).
There are no compatibility or security issues because they are precisely the same keys, just stored in a different way.
关于 compressed key 和 uncompressed key 等效性的相关测试请查看 ecdsa_tests.c 中的 test_kyk_ec_sig_verify() 测试.
[29] https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Difficulty Difficulty
[30] https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1DQYQOLsB-pJWGu5e8CXF4vkxdYHEJDOyxQptBmC_030/edit#gid=0 Bitcoin Difficulty Adjustments Data Table
[31] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bloom_filter Bloom 过滤器